0x00 准备
- 阅读MapReduce论文
- 配置GO环境
因为之前没用过GO,所以 先在网上学了一下语法A Tour of Go
感觉Go的接口和方法的语法和C++挺不一样, 并发编程也挺有意思
0x01 MapReduce简介
需要实现master和coordinator。
MapReduce分为两个阶段:Map和Reduce阶段。
Map阶段函数提供Key,比如pg-being_ernest.txt是key,然后Worker通过这个Key获取Value。比如pg-being_ernest.txt的具体内容。然后将Key和Value(在例子中是文章的内容),传递给map function。获取结果,并将结果分成R个Reduce内容。
举个例子。假设我们要对pg-being_ernest.txt和pg-dorian_gray.txt统计词频。那么就要有两个Map Task(不一定有两个Worker,比如有3个Worker,那么就是2个Worker干活一个围观;如果只有一个Worker,那么该Worker会被前后分配两次Map操作)。假设有3个Reduce操作,那么Map的中间操作就会按照key被分为3个文件。
pg-being_ernest.txt对应Map0 , Map0操作的kv被分进mr-0-0,mr-0-1,mr-0-2
pg-dorian_gray.txt对应Map0 , Map0操作的kv被分进mr-1-0,mr-1-1,mr-1-2
当所有的Mapf已经生成结果,Worker就会被指派Reduce操作。比如被指派的Reduce操作编号为2,那么Reduce就会读取mr-0-2,mr-1-2。并且聚合相同的Key,传递给Reduce函数。
比如,pg-being_ernest.txt中的map操作有kv,a 1 b 1 b 1输出到mr-0-2。pg-dorian_gray.txt中的map操作有kv,c 1 b 1 c 1输出到mr-0-2。
然后Task编号为2的Reduce任务会读取所有对应的中间文件。得到key。a 1 b 1 b 1 c 1 b 1 c 1。然后再对要处理的key进行排序,得到 a 1 b 1 b 1 b 1 c 1 c 1。再按照相同的key调用reduce函数。
上面例子的调用为
reducef(key:"a",value:list[1]),得到"1"
reducef(key:"b",value:list[1,1,1]),得到"3"
reducef(key:"c",value:list[1,1]),得到"2"最后将kvs:[{“a”,“1”},{“b”,“3”},{“c”,“2”}]写入该reduce生成的文件
mr-out-2
0x02 RPC
使用GO的RPC库,可以简单地实现Server
学习时参考了Go 每日一库之 rpc - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
在MapReduce操作流程中就是:
- 首先启动多个Worker(以下简称C)和一个Coordinator(以下简称S)
- C每隔一段时间(比如1s)会向S发送一个任务请求
- S首先检查Map任务还有没有分配完(注意不是运行完)。如果没有,分配一个Map任务给C
- 如果Map任务分配完了,并且还没有工作完,S让C等待
- 如果Map工作完了。Reduce还没分配完了,S给C分配一个空闲的Reduce任务
- 如果Reduce都工作完了,所有任务也都结束了。
- 如果C完成了任务,会向S发送一个请求。S知道了某个任务完成,就会进行相应的操作标记。
一些注意的点:
每个任务是有时间上限的(10s)。每分配一个任务就会启动一个GO程,然后等待相应的时间,检查是否完成了工作。如果没完成,将该任务编号重新加入管道。
如何判断一个任务是否完成呢?
比如第一个Worker申请到了任务1,过了10s钟还没有完成,S又将任务1加入待完成管道。此时第2个worker申请到了任务1,又过了4s,第一个Worker发送一个MapDone的请求给S。S如何判断是否完成了该任务。
我的处理是维护任务是由哪个Worker运行的状态。其中Worker由RPC的时间戳标记。比如worker1在第一次请求时时间戳为13213123,Server维护maptask[1]是由13213123正在运行,当第一次超时,maptask[1]变成了worker2请求时的时间戳``13219889。在第14s,收到MapDone的请求,检查其时间戳为13213123`和当前正在运行的时间戳不同,所以丢弃掉该结果。
还有就是并发处理,这个使用锁就行了。
0x03 调试
- 命令行的参数:(因为不用shell的话不能用通配符pg*.txt代替,只能输入所有文件名)
pg-being_ernest.txt
pg-dorian_gray.txt
pg-frankenstein.txt
pg-grimm.txt
pg-huckleberry_finn.txt
pg-metamorphosis.txt
pg-sherlock_holmes.txt
pg-tom_sawyer.txt
- 在调试时出现报错
cannot load plugin ./wc.so err: plugin.Open("./wc"): plugin was built with a different version of package internal/abi
是因为build wc.so时的参数和运行mr参数不一致导致的。
- 使用
./test-mr-many.sh 3重复测试3次。通过测试
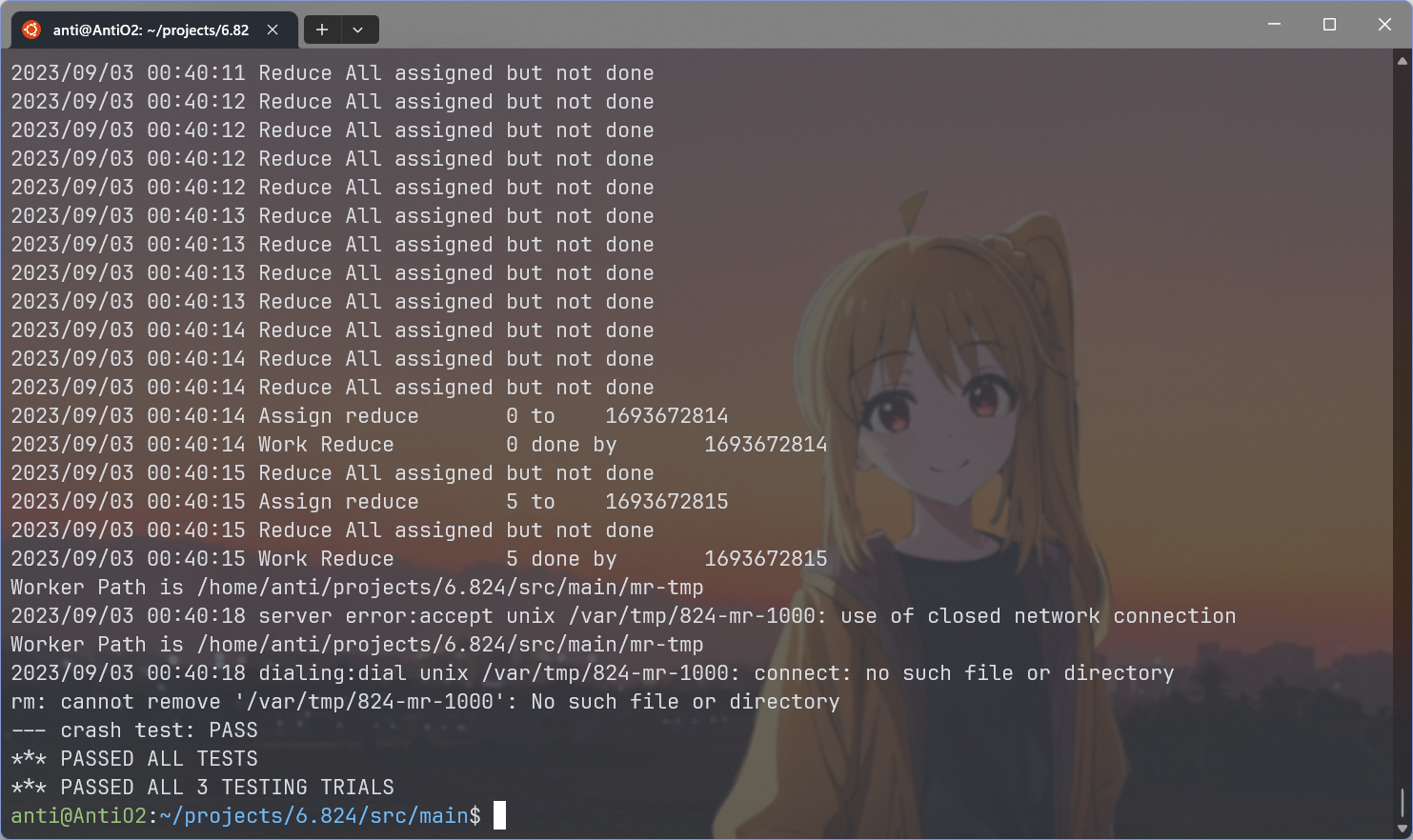
感觉Lab1做下来还是挺通透。像是引入GO和相关概念。通过lab,学习到了GO调试。
0x04 代码
coordinator.go
package mr
import (
"log"
"sync"
"time"
)
import "net"
import "os"
import "net/rpc"
import "net/http"
type status int // 用于指示worker的状态
const (
notStart status = iota
running
taskDone
)
const workMaxTime = 12 * time.Second
type Coordinator struct {
// Your definitions here.
nReduce int // Reduce数量
mMap int // Map数量
taskDone bool
reduceTaskStatus []status
mapTaskStatus []status
// runningMap 是当前正在running的rpcId
// 想一下这种情况:第一个worker没有在10秒内返回结果,于是master开始把同样的任务返回给了第二个worker,此时又过了几秒,比如两秒钟
// 那么master如何判断是第二个worker完成了任务,还是第一个worker呢?
runningMap []RpcIdT
runningReduce []RpcIdT
mapTasks chan TaskIdT // 待开始的map
reduceTasks chan TaskIdT // 待开始的reduce
files []string // 要进行task的文件
mapCnt int // 已完成的map数量
reduceCnt int // 已完成的reduce数量
latch *sync.Cond
}
// Your code here -- RPC handlers for the worker to call.
// Example
// an example RPC handler.
//
// the RPC argument and reply types are defined in rpc.go.
func (c *Coordinator) Example(args *ExampleArgs, reply *ExampleReply) error {
reply.Y = args.X + 1
return nil
}
// Appoint 用于worker请求一个任务
func (c *Coordinator) Appoint(request *ReqArgs, reply *ResArgs) error {
reply.ResId = request.ReqId
reply.MapNumM = c.mMap
reply.ReduceNumN = c.nReduce
c.latch.L.Lock()
done := c.taskDone
c.latch.L.Unlock()
if done {
reply.ResOp = WorkDone
return nil
}
switch request.ReqOp {
case WorkReq:
{
// 请求一个任务
c.latch.L.Lock()
if len(c.mapTasks) > 0 {
// 如果map任务还没有完全分配 分配一个map worker
taskId := <-c.mapTasks
reply.ResTaskId = taskId
reply.ResContent = c.files[taskId]
reply.ResOp = WorkMap
c.runningMap[taskId] = reply.ResId
c.mapTaskStatus[taskId] = running
c.latch.L.Unlock()
go c.checkDone(WorkMap, reply.ResTaskId)
log.Printf("Assign map \t%d to \t%d\n", reply.ResTaskId, reply.ResId)
return nil
}
if c.mapCnt < c.mMap {
// 如果map任务已经全部分配完了,但是还没有运行完成,还不能开始reduce
// worker需要暂时等待一下
reply.ResOp = WorkNothing
c.latch.L.Unlock()
log.Println("Map All assigned but not done")
return nil
}
if len(c.reduceTasks) > 0 {
// 已经确定完成了所有map,还没有分配完reduce
taskId := <-c.reduceTasks
reply.ResTaskId = taskId
reply.ResOp = WorkReduce
c.runningReduce[taskId] = reply.ResId
c.reduceTaskStatus[taskId] = running
c.latch.L.Unlock()
go c.checkDone(WorkReduce, reply.ResTaskId)
log.Printf("Assign reduce \t%d to \t%d\n", reply.ResTaskId, reply.ResId)
return nil
}
// 如果分配完了所有的reduce,但是还没有done.worker需要等待
reply.ResOp = WorkNothing
log.Println("Reduce All assigned but not done")
c.latch.L.Unlock()
return nil
}
case WorkMapDone:
{
c.latch.L.Lock()
defer c.latch.L.Unlock()
if c.runningMap[request.ReqTaskId] != request.ReqId || c.mapTaskStatus[request.ReqTaskId] != running {
// 说明该map已经被abort
reply.ResOp = WorkTerminate
return nil
}
log.Printf("Work Map \t%d done by \t%d\n", request.ReqTaskId, request.ReqId)
c.mapTaskStatus[request.ReqTaskId] = taskDone
c.mapCnt++
}
case WorkReduceDone:
{
c.latch.L.Lock()
defer c.latch.L.Unlock()
if c.runningReduce[request.ReqTaskId] != request.ReqId || c.reduceTaskStatus[request.ReqTaskId] != running {
// 说明该map已经被abort
reply.ResOp = WorkTerminate
return nil
}
c.reduceTaskStatus[request.ReqTaskId] = taskDone
c.reduceCnt++
log.Printf("Work Reduce \t%d done by \t%d\n", request.ReqTaskId, request.ReqId)
if c.reduceCnt == c.nReduce {
c.taskDone = true
reply.ResOp = WorkDone
}
}
default:
return nil
}
return nil
}
// start a thread that listens for RPCs from worker.go
func (c *Coordinator) server() {
log.Println("Launching Server")
e := rpc.Register(c)
if e != nil {
log.Fatal("register error:", e)
}
rpc.HandleHTTP()
//l, e := net.Listen("tcp", ":1234")
sockname := coordinatorSock()
_ = os.Remove(sockname)
l, e := net.Listen("unix", sockname)
go func(l net.Listener) {
for {
time.Sleep(5 * time.Second)
if c.Done() {
err := l.Close()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("close error:", err)
}
}
}
}(l)
if e != nil {
log.Fatal("listen error:", e)
}
go func() {
err := http.Serve(l, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("server error:", err)
}
}()
}
// Done main/mrcoordinator.go calls Done() periodically to find out
// if the entire job has finished.
func (c *Coordinator) Done() bool {
c.latch.L.Lock()
defer c.latch.L.Unlock()
// Your code here.
return c.taskDone
}
// checkDone 检查任务是否完成
func (c *Coordinator) checkDone(workType WorkType, t TaskIdT) {
time.Sleep(workMaxTime)
c.latch.L.Lock()
defer c.latch.L.Unlock()
switch workType {
case WorkMap:
{
if c.mapTaskStatus[t] != taskDone {
c.mapTaskStatus[t] = notStart
c.mapTasks <- t
}
}
case WorkReduce:
{
if c.reduceTaskStatus[t] != taskDone {
// 如果没有完成任务
c.reduceTaskStatus[t] = notStart
c.reduceTasks <- t
}
}
default:
log.Panicf("Try Check Invalid WorkType %v\n", workType)
}
}
// MakeCoordinator create a Coordinator.
// main/mrcoordinator.go calls this function.
// nReduce is the number of reduce tasks to use.
func MakeCoordinator(files []string, nReduce int) *Coordinator {
log.Println("Launching Master Factory")
c := Coordinator{}
c.nReduce = nReduce
c.mMap = len(files) // 每个file对应一个map
c.taskDone = false
c.files = files
c.mapTasks = make(chan TaskIdT, c.mMap)
c.mapTaskStatus = make([]status, c.mMap)
c.runningMap = make([]RpcIdT, c.mMap)
c.reduceTaskStatus = make([]status, nReduce)
c.reduceTasks = make(chan TaskIdT, nReduce)
c.runningReduce = make([]RpcIdT, nReduce)
c.latch = sync.NewCond(&sync.Mutex{})
for i := 0; i < c.mMap; i++ {
c.mapTasks <- TaskIdT(i)
c.runningMap[i] = -1
c.mapTaskStatus[i] = notStart
}
for i := 0; i < c.nReduce; i++ {
c.reduceTasks <- TaskIdT(i)
c.runningReduce[i] = -1
c.reduceTaskStatus[i] = notStart
}
c.server()
return &c
}
rpc.go
package mr
//
// RPC definitions.
//
// remember to capitalize all names.
//
import "os"
import "strconv"
//
// example to show how to declare the arguments
// and reply for an RPC.
//
type ExampleArgs struct {
X int
}
type ExampleReply struct {
Y int
}
type RpcIdT int64 // RpcIdT 是通过时间戳生成的, 指示一个唯一的RpcId
type ReqArgs struct {
ReqId RpcIdT
ReqOp WorkType
ReqTaskId TaskIdT
}
// ResArgs 是RPC的返回
// Response
type ResArgs struct {
ResId RpcIdT
ResOp WorkType
ResTaskId TaskIdT // 分配的任务编号
ResContent string
ReduceNumN int // 有n个reduce
MapNumM int // 有M个map任务
}
type WorkType int
// TaskIdT 是对任务的编号
type TaskIdT int
// 枚举工作类型
const (
WorkNothing WorkType = iota
WorkReq // worker申请工作
WorkMap // 分配worker进行map操作
WorkReduce // 分配worker进行reduce操作
WorkDone // [[unused]]master所有的工作完成
WorkTerminate // 工作中止
WorkMapDone // Worker完成了map操作
WorkReduceDone // Worker完成了reduce操作
)
// Rpc exports struct we need
type Rpc struct {
Req ReqArgs
Res ResArgs
}
// Cook up a unique-ish UNIX-domain socket name
// in /var/tmp, for the coordinator.
// Can't use the current directory since
// Athena AFS doesn't support UNIX-domain sockets.
func coordinatorSock() string {
s := "/var/tmp/824-mr-"
s += strconv.Itoa(os.Getuid())
return s
}
worker.go
package mr
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"io"
"os"
"sort"
"strconv"
"time"
)
import "log"
import "net/rpc"
import "hash/fnv"
const sleepTime = 500 * time.Millisecond
// KeyValue
// Map functions return a slice of KeyValue
type KeyValue struct {
Key string
Value string
}
type ByKey []KeyValue
// Len 通过HashKey进行排序
func (a ByKey) Len() int { return len(a) }
func (a ByKey) Swap(i, j int) { a[i], a[j] = a[j], a[i] }
func (a ByKey) Less(i, j int) bool { return ihash(a[i].Key) < ihash(a[j].Key) }
// use ihash(key) % NReduce to choose the reduce
// task number for each KeyValue emitted by Map.
func ihash(key string) int {
h := fnv.New32a()
_, err := h.Write([]byte(key))
if err != nil {
return 0
}
return int(h.Sum32() & 0x7fffffff)
}
// Worker
// main/mrworker.go calls this function.
func Worker(mapf func(string, string) []KeyValue,
reducef func(string, []string) string) {
// Your worker implementation here.
for {
timeStamp := time.Now().Unix()
rpcId := RpcIdT(timeStamp)
req := ReqArgs{}
req.ReqId = rpcId
req.ReqOp = WorkReq // 请求一个工作
res := ResArgs{}
ok := call("Coordinator.Appoint", &req, &res)
if !ok {
// 如果Call发生错误
log.Println("Maybe Coordinator Server has been closed")
return
}
switch res.ResOp {
case WorkDone:
// 所有工作已经完成
return
case WorkMap:
doMap(rpcId, &res, mapf)
case WorkReduce:
doReduce(rpcId, &res, reducef)
case WorkNothing:
// 等待
time.Sleep(sleepTime)
default:
break
}
time.Sleep(sleepTime)
}
}
func doMap(rpcId RpcIdT, response *ResArgs, mapf func(string, string) []KeyValue) {
// filename 是response中的文件名
filename := response.ResContent
file, err := os.Open(filename)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot open %v", filename)
}
defer func(file *os.File) {
_ = file.Close()
}(file)
// content读取该文件中的所有内容
content, err := io.ReadAll(file)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot read %v", filename)
}
kvs := mapf(filename, string(content))
// 需要将kv输出到n路 中间文件中
ofiles := make([]*os.File, response.ReduceNumN)
encoders := make([]*json.Encoder, response.ReduceNumN)
for i := 0; i < response.ReduceNumN; i++ {
// 这里输出的名字是mr-ResTaskId-reduceN
// 其中,ResTaskId是0~m的数字
oname := "mr-" + strconv.Itoa(int(response.ResTaskId)) + "-" + strconv.Itoa(i)
ofiles[i], err = os.Create(oname)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("Can't Create Intermediate File: ", oname)
}
defer func(file *os.File, oname string) {
err := file.Close()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("Can't Close Intermediate File", oname)
}
}(ofiles[i], oname)
encoders[i] = json.NewEncoder(ofiles[i])
}
for _, kv := range kvs {
ri := ihash(kv.Key) % response.ReduceNumN
err := encoders[ri].Encode(kv)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("Encode Error: ", err)
return
}
}
req := ReqArgs{
ReqId: rpcId,
ReqOp: WorkMapDone,
ReqTaskId: response.ResTaskId,
}
res := ResArgs{}
call("Coordinator.Appoint", &req, &res)
}
func doReduce(rpcId RpcIdT, response *ResArgs, reducef func(string, []string) string) {
rid := response.ResTaskId // 当前reduce的编号
var kva []KeyValue
for i := 0; i < response.MapNumM; i++ {
// 读取所有该rid的中间值
func(mapId int) {
// 读取m-rid的中间值
inputName := "mr-" + strconv.Itoa(i) + "-" + strconv.Itoa(int(rid))
// 在当前对应r的输出中,获取所有key
ifile, err := os.Open(inputName)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("Can't open file: ", inputName)
}
defer func(file *os.File) {
err := file.Close()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("Can't close file: ", inputName)
}
}(ifile)
dec := json.NewDecoder(ifile)
for {
var kv KeyValue
if err := dec.Decode(&kv); err != nil {
break
}
kva = append(kva, kv) //
}
}(i)
}
// 通过hashKey排序
sort.Sort(ByKey(kva))
intermediate := kva[:]
oname := "mr-out-" + strconv.Itoa(int(rid))
ofile, err := os.Create(oname)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("Can't create file: ", oname)
}
defer func(ofile *os.File) {
err := ofile.Close()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("Can't close file: ", oname)
}
}(ofile)
// log.Println("Total kv len: ", len(intermediate))
// cnt := 0
i := 0
for i < len(intermediate) {
j := i + 1
for j < len(intermediate) && intermediate[j].Key == intermediate[i].Key {
j++
}
var values []string
for k := i; k < j; k++ {
values = append(values, intermediate[k].Value)
}
// cnt++
output := reducef(intermediate[i].Key, values)
// this is the correct format for each line of Reduce output.
_, fprintf := fmt.Fprintf(ofile, "%v %v\n", intermediate[i].Key, output)
if fprintf != nil {
return
}
i = j
}
// log.Println("Unique key count: ", cnt)
req := ReqArgs{
ReqId: rpcId,
ReqOp: WorkReduceDone,
ReqTaskId: response.ResTaskId,
}
res := ResArgs{}
call("Coordinator.Appoint", &req, &res)
}
// CallExample
// example function to show how to make an RPC call to the coordinator.
//
// the RPC argument and reply types are defined in rpc.go.
func CallExample() {
// declare an argument structure.
args := ExampleArgs{}
// fill in the argument(s).
args.X = 99
// declare a reply structure.
reply := ExampleReply{}
// send the RPC request, wait for the reply.
call("Coordinator.Example", &args, &reply)
// reply.Y should be 100.
fmt.Printf("reply.Y %v\n", reply.Y)
}
// send an RPC request to the coordinator, wait for the response.
// usually returns true.
// returns false if something goes wrong.
func call(rpcName string, args interface{}, reply interface{}) bool {
// c, err := rpc.DialHTTP("tcp", "127.0.0.1"+":1234")
sockname := coordinatorSock()
c, err := rpc.DialHTTP("unix", sockname)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("dialing:", err)
}
defer func(c *rpc.Client) {
err := c.Close()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("Close Client Error When RPC Calling", err)
}
}(c)
err = c.Call(rpcName, args, reply)
if err == nil {
return true
}
fmt.Println(err)
return false
}